CPU Sockets - Basics
Knowledge Gainer
- Professor
- Oct 17, 2022
- Knowledge Gainer
CPU Sockets - Basics
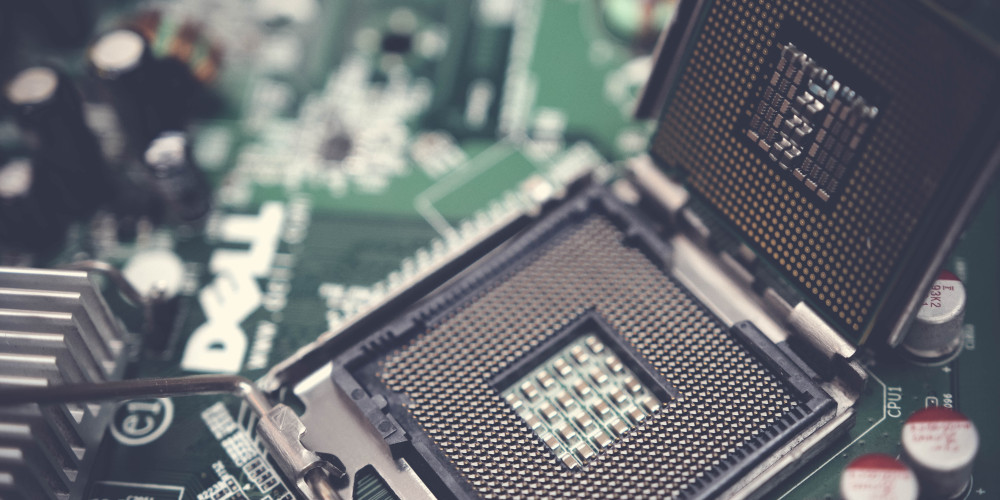
We have heard of motherboard. A motherboard is the largest printed circuit board in the computer. On this motherboard all other components are placed and connected to using circuits. The central processing unit (CPU) is also placed on this board. The CPU has pins and connectors that are then attached to motherboard. A CPU socket uses thousands of metal pins as contact points to allow power and data to be passed between the CPU and the motherboard.
It may be called CPU Socket or CPU slot interchangeably. This is a built in interface on motherboard at the time of designing and manufacturing. Look at the CPU socket type information for, if you want to replace or find a compatible CPU for your motherboard.
Manufacturers as Intel, AMD have created set of sockets and slot for their processors. So how many of type of sockets are there. Any processor before it is installed in the computer must match the socket available on the base motherboard. There are four types of sockets, namely
- LGA Sockets : Land Grid Array. In this type of socket the pins are available in the socket, and metallic contacts available on the lower area of the processor. The processor sits directly on the pins, and connection is formed. Many Intel sockets have seen LGA types, such as the LGA 1150, LGA 1155, or LGA 1200. AMD also uses in some cases. LGA sockets have less leakage currents.

- PGA Sockets : Pin Grid Array. These are rectangular or square in shape, and have pins aligned in a regular matrix. The holes in the socket holds processor tightly when handle is in place. This allows better retention and holding of pins when inserting the processor in the socket. This configuration allows the motherboard socket to be stronger because the pins go into the processor. It is the typical AMD socket, from Athlon’s socket A to Ryzen’s AM4.

-
ZIF Sockets : Zero Insertion Force. This is furtherance to PGA type socket, where the pins are carried by the microprocessor and inserted into the socket connectors. This mechanism is defined by not exerting any pressure (Zero Insertion Force) when installing or removing the processor from the socket, and uses a lever as a safety device. For CPU chips with many pins, the ZIF type of CPU sockets is preferred.
-
BGA Sockets : Ball Grid Array, when it comes to system-on-chip, this kind of socket is used. We cannot really call this as a socket, since the fixture on it is a permnanent one. ARM, Broadcom, Qualcomm, Nvidia, and other SoC manufacturers rely heavily on BGAs. The processors are soldered on to this socket, and hence replacement is almost not feasible.
At the physical level, all sockets differ in size and shape, processor architecture, number of contacts, type, and location. In addition, they also differ in the mounting of the processor cooling system.
More to come on sockets, and details.